-
Fibre Optic BroadbandWhat is fibre optic broadband?
This is about using the extraordinary capabilities of optical fibre as a transmission medium to transfer huge amounts of data speedily with very little interference. The transmission rate is higher than traditional copper-based broadband. Theoretically, optical fibre technology can deliver over 10,000Mbps of bandwidth. Home users are generally able to access network specifications of up to 10,000Mbps, depending on network rollout, for a faster internet experience.
Fibre optic broadband technology can be generally called FTTX, depending where the fibre terminates at, which can be:
- FTTC – Fibre-to-the-Curb
- FTTP – Fibre-to-the-Premises
- FTTB – Fibre-to-the-Building
- FTTH – Fibre-to-the-Home
- FTTR – Fibre-to-the-Room
FTTB (Fibre-to-the-Building)Optical fibre runs to the building and terminates at the building's engine room, which in turn is connected to a residence by a copper "twisted pair" telephone line.
FTTBFibreCopperxDSL Modem FTTH (Fibre-to-the-Home)
FTTH (Fibre-to-the-Home)Optical fibre runs to the building's engine room then on to a household's Optical Network Unit (ONU), with the end result that optical fibre runs all the way into the user's home. This is in turn the preferred architecture for delivering an optimized broadband bandwidth.
FTTHFibreFibre Modem How to Install Fibre-to-the-Home Broadband Service?Learn moreTelecommunication ExchangeTBELocal Telephone Duct RoomResidential BuildingApartment
How to Install Fibre-to-the-Home Broadband Service?Learn moreTelecommunication ExchangeTBELocal Telephone Duct RoomResidential BuildingApartment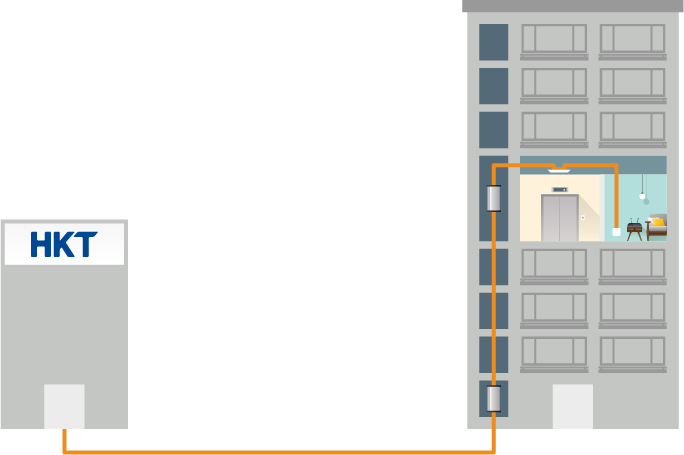 FTTR (Fibre-to-the-Room)
FTTR (Fibre-to-the-Room)Optical fibre runs to the building's engine room then on to a household's Optical Network Unit (ONU) and laying fibre in home to fulfill full fibre-based network coverage in every corner with Wi-Fi coverage.
FTTRFibreFibre ModemWi-Fi Fibre Router Fibre optic broadband benefits
Fibre optic broadband benefitsFibre-to-the-Home Broadband is an end-to-end fibre that runs from a telecommunications exchange, through underground cable ducting to a building main telecommunications and broadcasting equipment (TBE) room, and local telephone duct room, all the way to the first designated landing broadband socket in a customer home.
Increased upstream and downstream bandwidthFibre optic Internet connectivity can provide 100M or above bandwidth specification at equal upstream and downstream specification, without much limitation on distances due to its low loss characteristic. It is suitable for high-speed data transmission applications such as Internet TV with full high definition quality with surround sound, streaming full HD videos, uploading/downloading large files, or supporting cloud devices.
Steady transmission signalAs optical fibre transmits via light, the signal is not weakened easily and avoids electromagnetic interference. The signal is therefore very stable, ensuring high-quality broadband Internet access suitable for real-time high-definition multimedia services.
Note:
Bandwidth Specification refers to network specifications of the subscribed Services for the broadband line connected from the modem at your Premises to the first piece of network equipment or central office of the NETVIGATOR network. For Fibre-to-the-home Plans, bandwidth specifications of 100M, 200M, 300M, 500M, 1000M and 2500M correspond to a maximum upstream and downstream bandwidth of 100Mbps / 200Mbps / 300Mbps / 500Mbps / 1000Mbps / 2,500Mbps respectively. For bandwidth specification of 10,000M, maximum downstream bandwidth is 10,000Mbps and maximum upstream bandwidth is 10,000Mbps (the maximum upstream bandwidth is only applicable to new subscription of the service by consumer customers from October 5, 2020 onwards). The actual speed you experience using the Service will be less than the network specifications and affected by your device, technology, network and software used, network configuration and coverage, usage levels, international bandwidth and extraneous factors. -
Wireless InternetHome Wireless Modem Option
Many wireless routers are available on the market, but speed performance varies even if they all claimed to be complied with a particular wireless standard. Besides our peace-of-mind NETVIGATOR Home Wireless services, there are other wireless routers for your consideration if you decide to get one by yourself.
NETVIGATOR Home Wireless ServiceWith minimal rental fee, you can enjoy hassle-free home wireless service with our great service support.
- Single device : 2-in-1 wireless modem that support the function of both modem and wireless router.
- Service support : Onsite setup by our certified technician to ease all your hassle in setting up wireless network.
 NETVIGATOR's Home Wireless modem
Other Home Wireless modem options
NETVIGATOR's Home Wireless modem
Other Home Wireless modem optionsYou can setup your own wireless network by selecting from a wide range of wireless routers in the market based on your budget and requirements.
Modem & router : Router needs to be connected to the modem to form the wireless network.
Self deployment and configuration: Configure your own wireless network and setting. Make your own troubleshooting when there is wireless connection problem.
View the Home Networking Wireless Service suitable for fibre optic broadband service plan.
 Modem
Router
Wireless Internet access tips
Modem
Router
Wireless Internet access tipsFactors affecting wireless Internet access speeds and actual fibre optic broadband speeds are similar. However, when connected to a wireless network (Wi-Fi), Internet connection speeds may be influenced by the following two additional factors:
- Other wireless devices and your computer occupying the same area. If a wireless network operating frequency is similar to the frequency of another device (eg a microwave oven or wireless telephone), you may suffer interference or the wireless network connection could be blocked. Get a better connection by turning off other wireless devices to avoid interference.
- The distance of a wireless access point or router's location in relation to the computer, and physical obstacles could possibly affect network connection quality. Improve your connectivity speed by getting as close to the access point/router as possible, and make sure no physical obstacles, such as a wall, come between the access point/router and computer.
-
Measuring Internet SpeedHow to calculate broadband speed
Many users believe their broadband service is slower than advertised because they misunderstand the units of broadband speed. So let's see how this is calculated:
Theoretically, B represents "Byte" and b represents "bit" in transmission unit. Both have different definitions (see conversion table below):
1 Byte = 8 bits
1 Kb = 1024 bits
1 KB = 1024 bytes (= 8192 bits)
1 Mb = 1024 kb
1 MB = 1024 KB (= 8192 kb)
Note that the advertised broadband services "bandwidth" normally refers to the Network Specification. There are transmission overheads for the Ethernet protocols, as well as other factors affecting the actual data throughput.
Factors affecting actual speed of fibre optic broadbandActual Internet access speed is affected by multiple factors, so is less than network specifications might suggest. Common influencing factors are:
Computer configurationPoor computer performance is a common reason for slow speeds. You can get more details on recommended computer configuration by referring to System requirements
Multiple devices connected simultaneously to same networkWhen multiple connected computers or devices – such as a mobile phone and wireless router – connect simultaneously to the same network, the result of having to share the available bandwidth, Internet access speed could be reduced.
Wireless router specification is extremely important in this regard. If a router that does not support high speed is connected, Internet access speed will be correspondingly reduced. For example, if you are using 10,000M fibre optic broadband service and your wireless router only supports up to 1000Mbps, the highest possible Internet access speed will only reach up to about 1000Mbps.Wireless networkWireless connection throughput is subject to conditions such as the local radio environment, number of devices sharing the same wireless network, range of the wireless coverage, interferences, physical obstacles and capability of receiving end. As a result, actual wireless connection speed will be less than the maximum throughput.
Many users enjoy internet access via wireless routers. However, with many options of wireless routers available in the market, you may find it useful to refer to overview and features of Home Wireless Service for details and specifications of some models we recommend and choose the suitable one for your broadband.Transmission bandwidth of network server and network conditionEach website is served by a server connected to the network, and network bandwidth is distributed according to a website's usage. So when the number of users is low, your connection speed will be faster. In contrast, when the number of simultaneous users is high, your linking network server will be congested, causing the connection speed to drop, especially for an overseas network server and the amount of users.
Utilization of other instrument or softwareInternet connection speeds differ and depend on what other services are being used at the same time – e.g. web browsing, internet television and so on. Bandwidth demanding applications such as file sharing, video conferencing, and watching online movies, and software used will also influence internet access speeds, as they consume bandwidth, as well as processing power of your computer.
Broadband speed testPreparation before testing- Check your computer system configuration. Please refer to recommended system requirement.
- Ensure the computer is the sole active device on your office or home network. Turn off other computers, IPTV set-top-boxes, NAS and so on.
- Close any other applications and any application running in the background.
- Connect the computer directly to your modem with CAT5e Ethernet cable, bypassing any wired or wireless router.
- Update the LAN card driver, web browser and programmes for viewing multimedia and streaming video and audio, such as Flash Player to the latest versions.
Recommended test websiteWe recommend the www.myspeedmeter.net speed test website. If you have any inquiries on the speed test platform, please contact the website administrator directly.
System requirementsGet the best out of NETVIGATOR's ultra fast and stable home broadband service by adopting the following recommended PC configuration.
-
Requirements for 1.5M/3M/6M/8M/18M/30MPC Platforms Requirements
-
Operating systems supported:
.Windows 7 (32-bit or 64-bit) or above -
Processor:
.1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) processor -
System Memory:
.1 gigabyte (GB) RAM (32-bit) or 2 GB RAM (64-bit) -
Hard Drive:
.16 GB available hard disk space (32-bit) or 20 GB (64-bit) -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (10/100/1000BaseT) or Wireless 802.11b/g/n if using a Wireless Modem
Mac Platforms Requirements-
Operating systems supported:
.OS X v10.6.8 or later -
Processor:
.Intel Core 2 Duo, Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 or higher -
System Memory:
.2GB of memory or more -
Hard Drive:
.8GB of available space -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (10/100/1000BaseT) or Wireless 802.11b/g/n if using a Wireless Modem
-
Operating systems supported:
-
Requirements for 100M/200M/300MPC Platforms Requirements
-
Operating systems supported:
.Windows 7 (64-bit) or above -
Processor:
.Core i5 or above -
System Memory:
.2 gigabyte (GB) RAM or more -
Hard Drive:
.20 GB available hard disk space -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (100/1000BaseT)
Mac Platforms Requirements-
Operating systems supported:
.OS X v10.6.8 or later -
Processor:
.Intel Core 2 Duo, Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 or higher -
System Memory:
.4GB of memory or more -
Hard Drive:
.8GB of available space, SSD for 500M/100M connection -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (100/1000BaseT)
-
Operating systems supported:
-
Requirements for 500M/1000M/2x1000M Multi-Use /4x1000M Multi-UsePC Platforms Requirements
-
Operating systems supported:
.Window 10 (64-bit) or above -
Processor:
.8th gen Core i5 or above -
System Memory:
.4 gigabyte (GB) RAM -
Hard Drive:
.20 GB available hard disk space, SSD, PCI-E interface -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (100/1000BaseT)
Mac Platforms Requirements-
Operating systems supported:
.OS v10.14 or later -
Processor:
.8th gen Core i5 or above -
System Memory:
.4GB of memory or more -
Hard Drive:
.20 GB available hard disk space, PCIe SSD -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (100/1000BaseT)
-
Operating systems supported:
-
Requirements for 2500M/ 2500M + 1000M Multi-UsePC Platforms Requirements
-
Operating systems supported:
.Window 10 (64-bit) or above -
Processor:
.10th gen Core i5 or above -
System Memory:
.8 GB RAM -
Hard Drive:
.20 GB available hard disk space, PCIe SSD -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (2,500Mbps BaseT)
Mac Platforms Requirements-
Operating systems supported:
.OS v11.0 or later -
Processor:
.Apple M1 or above -
System Memory:
.8 GB RAM -
Hard Drive:
.20 GB available hard disk space, PCIe SSD -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (2,500Mbps BaseT)
-
Operating systems supported:
-
Requirements for 10,000MPC Platforms Requirements
-
Operating systems supported:
.Window 10 (64-bit) or above -
Processor:
.10th gen Core i5 or above -
System Memory:
.8 GB RAM -
Hard Drive:
.20 GB or above, PCIe SSD interface -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (10G BaseT)
Mac Platforms Requirements-
Operating systems supported:
.OS v11.0 or later -
Processor:
.Apple M1 or above -
System Memory:
.8 GB RAM -
Hard Drive:
.20 GB or above, PCIe SSD interface -
Required connection ports:
.Ethernet port (2,500Mbps BaseT)
-
Operating systems supported:
-
Requirements for 50,000MRequirements of 50,000M
-
Operating systems supported:
.Window 11 Pro or above -
Processor:
.13th gen Core i7 or above -
System Memory:
.32GB RAM -
Hard Drive:
.256GB M2 or above -
Required connection ports:
.PCIe 25G port (SPF28+) or Thunderbolt 3/4 (SPF28+ adapter)
Mac Platforms Requirements-
Operating systems supported:
.OS v15.0 or later -
Processor:
.Apple M3 or above -
System Memory:
.32GB RAM -
Hard Drive:
.256GB M2 or above -
Required connection ports:
.PCIe 25G port (SPF28+) or Thunderbolt 3/4 (SPF28+ adapter)
-
Operating systems supported:
-
What is VLAN?
VLAN stands for virtual local area network and is a technology by which multiple virtual circuits are created on a physical network for the logical grouping of different devices. Traffic passes through each VLAN circuit in a totally independent manner. Traffic segregation means congestion on one circuit is avoided when huge volumes of data pass through other virtual circuits. VLAN improves protection of devices and grants superior control over network resources by separating different applications.
VLAN has been serving commercial broadband deployments for quite some time and delivers network management and security advantages. NETVIGATOR's Multi-Use Broadband Service is based on VLAN technology, which has improved the overall high-speed broadband user experience.
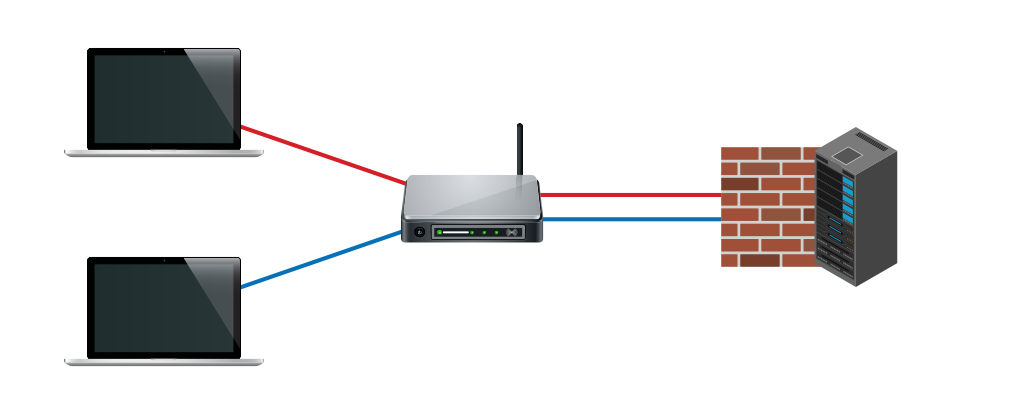
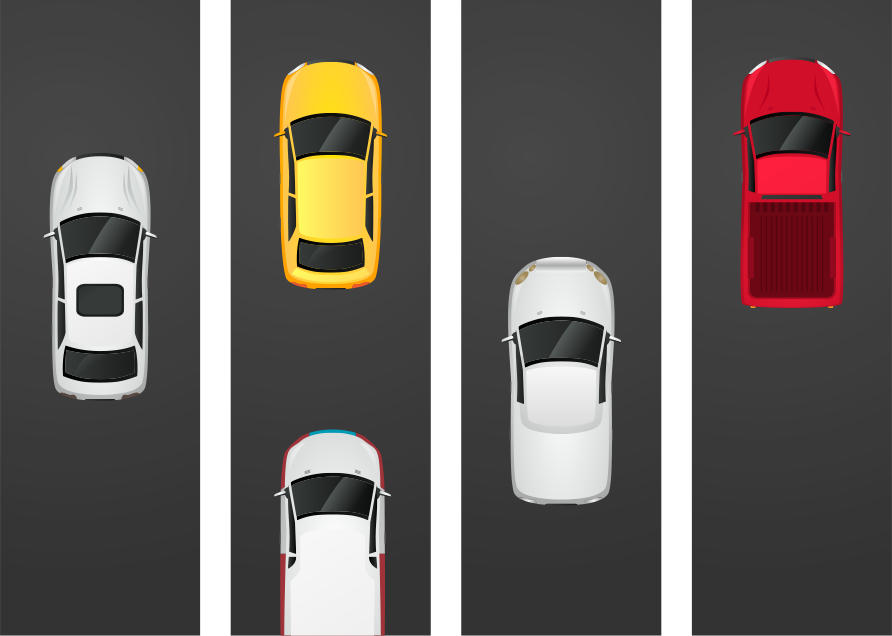 with VLAN
with VLAN
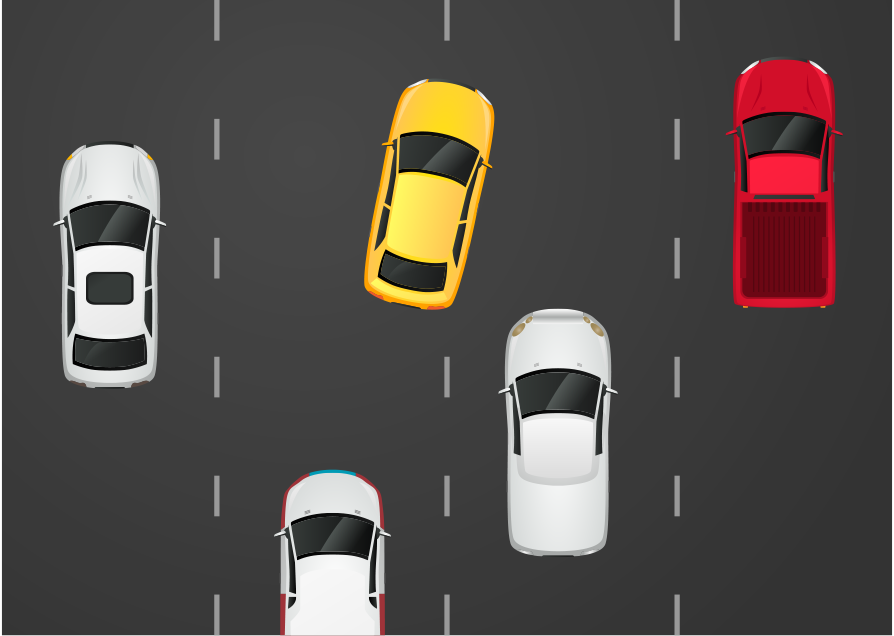 without VLAN
VLAN featuresSecurity improvement
without VLAN
VLAN featuresSecurity improvementVLANs' network segmentation technology creates a collection of isolated circuits. When properly configured, VLAN segmentation helps to thwart attacks on a system.
Meanwhile, inter-VLAN communication requires traffic routing by using an operator's network equipment, which is usually protected by a firewall or access-list control. VLAN segregation therefore fends off computer viruses and malware to enhance network security.
 VLAN
VLAN
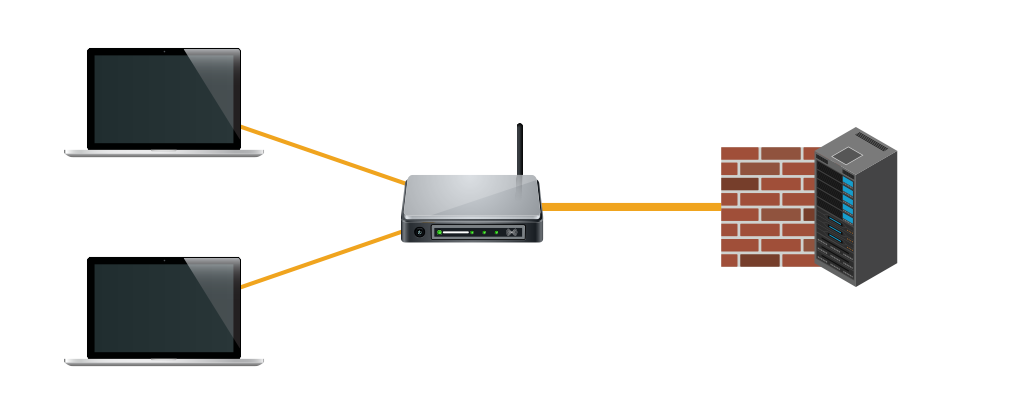 without VLAN
Ensure performance of segregated circuit
without VLAN
Ensure performance of segregated circuitVLANs' network segmentation technology creates a collection of isolated circuits, whereby each VLAN circuit operates individually, and transfer of data is not is allowed between VLANs. This approach optimizes network performance and ensures users enjoy smooth-running and low-latency network when playing online games or making voice and video calls.
Different settings for different users and applicationsA network behaves differently according to whether a VLAN is enabled or not. These differing characteristics suit the needs of disparate user groups and applications.
An enabled VLAN is suitable for users and applications requiring- Greater security
- High-quality segregated circuits for gaming and similar activity
- A home office or server set up
A disabled VLAN is suitable for users and applications requiring- Home sharing – e.g. printer and multimedia
- Shared bandwidth flexibility
- Easy home network configuration and use
The VLAN setting is disabled by default for 2x1000M Multi-Use Plan, but enabled for 4x1000M Multi-Use Plan. Users can contact our Customer Service specialists to request VLAN setting changes whenever needed.
Note: VLANs create segregated networks such that each circuit operates independently. No data is transferred between VLANs, which may affect inter-VLAN activities such as sharing a printer or files. Bandwidth specification of Fibre-to-the-room plan corresponds to a maximum downstream and upstream bandwidth of 1000Mbps.
Broadband Corner
All you need to know about broadband fiber optic and Wi-Fi connectivity; and the tips of measuring internet speed.
Broadband Corner
